Dementia Fall Risk - The Facts
Dementia Fall Risk - The Facts
Blog Article
The 10-Second Trick For Dementia Fall Risk
Table of ContentsDementia Fall Risk Things To Know Before You BuyTop Guidelines Of Dementia Fall RiskGetting My Dementia Fall Risk To WorkMore About Dementia Fall Risk
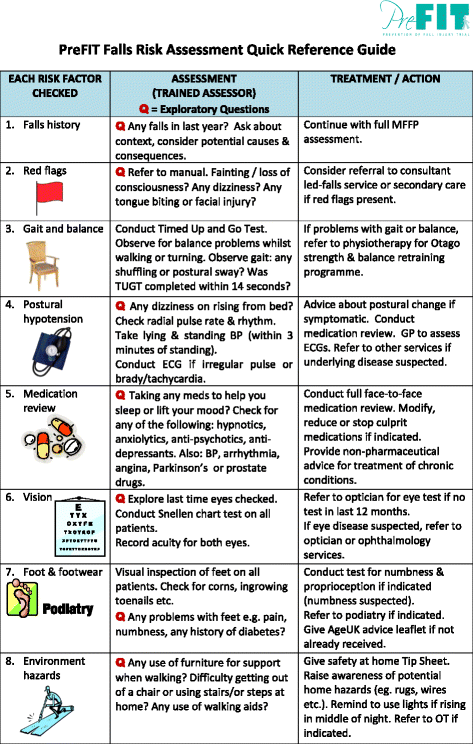
A fall risk analysis checks to see just how likely it is that you will certainly drop. The assessment generally includes: This includes a series of inquiries about your general wellness and if you've had previous drops or problems with equilibrium, standing, and/or walking.STEADI consists of testing, assessing, and treatment. Interventions are referrals that may reduce your danger of falling. STEADI includes three steps: you for your risk of succumbing to your danger elements that can be enhanced to try to stop drops (as an example, equilibrium troubles, damaged vision) to minimize your risk of dropping by making use of efficient strategies (for instance, giving education and sources), you may be asked several concerns including: Have you dropped in the past year? Do you really feel unstable when standing or walking? Are you bothered with falling?, your copyright will certainly evaluate your stamina, balance, and gait, using the complying with autumn assessment tools: This test checks your stride.
You'll sit down once again. Your supplier will certainly inspect the length of time it takes you to do this. If it takes you 12 secs or more, it may imply you are at greater risk for a fall. This examination checks strength and equilibrium. You'll sit in a chair with your arms went across over your chest.
The positions will obtain more difficult as you go. Stand with your feet side-by-side. Move one foot midway ahead, so the instep is touching the huge toe of your other foot. Relocate one foot totally in front of the various other, so the toes are touching the heel of your various other foot.
6 Simple Techniques For Dementia Fall Risk
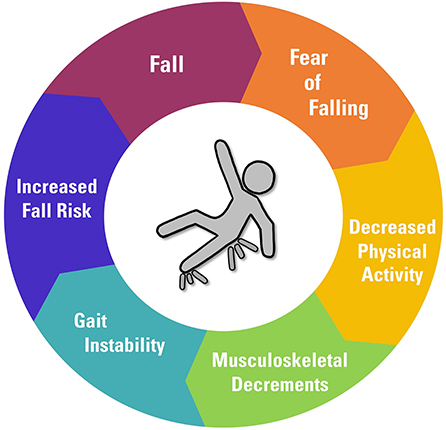
Most drops take place as an outcome of several adding aspects; therefore, handling the danger of dropping starts with determining the factors that add to drop risk - Dementia Fall Risk. Some of the most relevant risk factors include: Background of prior fallsChronic clinical conditionsAcute illnessImpaired gait and balance, lower extremity weaknessCognitive impairmentChanges in visionCertain risky drugs and polypharmacyEnvironmental variables can also boost the threat for falls, consisting of: Poor lightingUneven or harmed flooringWet or unsafe floorsMissing or damaged handrails and grab barsDamaged or incorrectly equipped equipment, such as beds, wheelchairs, or walkersImproper usage of assistive devicesInadequate guidance of individuals residing in the NF, including those who display aggressive behaviorsA successful autumn threat monitoring program needs a thorough clinical assessment, with input from all members of the interdisciplinary group
The treatment plan should likewise consist of treatments that are system-based, such as those that promote a secure atmosphere (proper illumination, handrails, grab bars, etc). The effectiveness of the interventions must be assessed occasionally, and the treatment strategy revised as necessary to show changes in the fall risk evaluation. Carrying out an autumn danger administration system making use of evidence-based best practice can reduce the occurrence of falls in the NF, while limiting the possibility for fall-related injuries.
Dementia Fall Risk Things To Know Before You Get This
The AGS/BGS standard recommends evaluating all adults matured 65 years and older for fall danger every year. This screening includes asking people whether they have fallen 2 or more times in the past year or sought clinical focus for a fall, or, if they have actually not fallen, whether they really feel unstable when strolling.
People that have dropped when without injury needs to have their balance and stride reviewed; those with gait or balance problems ought to receive additional analysis. A history of 1 fall without injury and without stride or equilibrium issues does not call for additional evaluation beyond continued annual fall risk screening. Dementia Fall Risk. A fall threat analysis is needed as component of the Welcome to Medicare assessment
Get This Report about Dementia Fall Risk
Recording a drops background is one of the top quality indicators for loss avoidance and administration. Psychoactive drugs in particular are investigate this site independent forecasters of drops.
Postural hypotension can commonly be minimized by reducing the dosage of blood pressurelowering medications and/or quiting medications that have orthostatic hypotension as a side impact. Usage of above-the-knee assistance hose pipe and sleeping with the head of the bed raised might additionally reduce postural reductions in high blood pressure. The recommended components of a fall-focused physical examination are shown in Box 1.
.png)
A yank time more than or equal to 12 secs recommends high fall risk. The 30-Second Chair Stand examination assesses reduced extremity toughness and balance. Being unable to stand from a chair of knee elevation without using one's arms indicates increased fall danger. The 4-Stage Equilibrium test evaluates static equilibrium by having the individual stand in 4 positions, each progressively more informative post challenging.
Report this page